Unleash the Power of Nature's Finest: Our Organic Skincare Collection
Stem cells represent a groundbreaking frontier in medicine, promising to transform our approach to treating a multitude of diseases. This blog explores the fascinating types of stem cells, their unique functions, and the latest advancements in stem cell technology that hold the potential to revolutionize healthcare. Additionally, we delve into the ongoing ethical debates surrounding their research and application, making a case for the responsible advancement of this powerful scientific field.
The Fascinating World of Stem Cells
What Are the Different Types of Stem Cells?
Stem cells are a unique type of cell that have the remarkable ability to develop into different cell types in the body. These cells come in various forms, each with their own distinct properties and potential.
Stem cells can be broadly classified into several categories based on their origin and potency:
- Embryonic stem cells: These stem cells are derived from the inner cell mass of an early-stage embryo, known as a blastocyst. They are considered pluripotent, meaning they can differentiate into nearly all cell types in the body, with the exception of the placenta and the umbilical cord.
- Adult stem cells: Also referred to as somatic stem cells, these cells are found in various tissues and organs throughout the body, such as the bone marrow, adipose tissue, and the brain. Adult stem cells are generally multipotent, meaning they can give rise to a limited range of cell types specific to the tissue or organ in which they reside.
- Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs): These are adult cells that have been genetically reprogrammed to revert to an embryonic-like pluripotent state. This is achieved through the introduction of specific genetic factors that "reprogram" the cells, effectively turning them into stem cells.
- Cord blood stem cells: These stem cells are harvested from the umbilical cord and placenta after childbirth. Cord blood stem cells are considered a valuable source of hematopoietic (blood-forming) stem cells, which can be used for transplantation and regenerative medicine.
How Do Stem Cells Function in the Body?
Stem cells play a crucial role in the maintenance, repair, and regeneration of various tissues and organs throughout the body. Their unique properties and abilities allow them to contribute to these vital processes in remarkable ways.
The primary functions of stem cells include:
- Self-renewal: Stem cells have the ability to divide and renew themselves, maintaining a pool of undifferentiated cells that can be called upon as needed.
- Differentiation: Stem cells can undergo a process called differentiation, where they transform into specialized cell types with specific functions, such as muscle cells, nerve cells, or blood cells.
- Tissue regeneration: Stem cells can migrate to sites of injury or damage and contribute to the repair and regeneration of tissues, helping to restore their normal structure and function.
- Immune system support: Certain types of stem cells, such as hematopoietic stem cells, can give rise to immune system cells, playing a role in the body's defense against diseases and infections.
- Paracrine signaling: Stem cells can secrete a variety of growth factors, cytokines, and other signaling molecules that can influence the behavior and function of surrounding cells, promoting tissue repair and regeneration.
What Makes Stem Cells Unique Compared to Other Cells?
Stem cells possess remarkable properties that set them apart from other cell types in the body. These unique characteristics are what make stem cells so valuable in the fields of medicine and scientific research.
Key features that distinguish stem cells include:
- Undifferentiated state: Stem cells are unspecialized cells that have not yet committed to a particular cell lineage or function. This undifferentiated state allows them to retain the potential to develop into various cell types.
- Self-renewal: Stem cells have the ability to divide and replicate themselves indefinitely, maintaining a constant supply of undifferentiated cells.
- Multipotency: Depending on their type, stem cells can differentiate into a variety of specialized cell types, with some being pluripotent (able to form nearly all cell types) and others being multipotent (able to form a limited range of cell types).
- Plasticity: Stem cells exhibit a remarkable degree of plasticity, meaning they can adapt and respond to various environmental cues and signals, which can trigger their differentiation into specific cell types.
- Regenerative potential: Stem cells play a crucial role in the body's natural healing and regenerative processes, contributing to the repair and replacement of damaged or diseased tissues.
The remarkable properties of stem cells have opened up exciting possibilities in the field of regenerative medicine, where researchers and clinicians are exploring ways to harness the power of these cells to treat a wide range of medical conditions. As our understanding of stem cell biology continues to deepen, the future holds great promise for the development of innovative stem cell-based therapies that can transform the way we approach healthcare.
The Transformative Power of Stem Cell Technology
What Are the Latest Advances in Stem Cell Technology?
Stem cell research has been at the forefront of scientific innovation, with researchers making remarkable strides in unlocking the incredible potential of these remarkable cells. From breakthroughs in cell reprogramming to groundbreaking discoveries in stem cell-based therapies, the field of stem cell technology is rapidly evolving.
Stem cell technology has undergone a remarkable transformation in recent years, with researchers exploring new and innovative ways to harness the power of these versatile cells.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): The development of iPSCs has revolutionized the field of stem cell research. These cells are created by reprogramming adult cells, such as skin or blood cells, into a pluripotent state, allowing them to differentiate into a wide range of cell types.
- Embryonic Stem Cell Advancements: While the use of embryonic stem cells remains a controversial topic, researchers have continued to make significant advancements in understanding and manipulating these cells. Breakthroughs in cell culture techniques and differentiation protocols have expanded the potential applications of embryonic stem cells.
- Directed Differentiation: Researchers have made significant progress in directing the differentiation of stem cells into specific cell types, such as neurons, cardiomyocytes, and pancreatic cells. This has opened up new avenues for disease modeling, drug testing, and regenerative medicine.
How Are Researchers Using Stem Cells to Treat Diseases?
The potential of stem cells to regenerate and replace damaged or dysfunctional tissues has captured the imagination of scientists and clinicians around the world. Researchers are actively exploring the use of stem cell-based therapies to tackle a wide range of medical conditions.
Stem cell-based therapies have emerged as a promising approach to treating various diseases and injuries.
- Neurodegenerative Disorders: Researchers are investigating the use of stem cells to replace lost or damaged neurons in conditions like Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and spinal cord injuries. By transplanting stem cell-derived neurons, the goal is to restore function and improve patient outcomes.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Stem cell-based therapies are being explored to regenerate damaged heart tissue and improve cardiac function in patients with conditions like heart failure and myocardial infarction. The ability of stem cells to differentiate into cardiomyocytes and support angiogenesis holds great promise.
- Diabetes: Stem cell-derived pancreatic beta cells are being explored as a potential treatment for diabetes, with the aim of restoring insulin production and glycemic control in affected individuals.
What Role Do Stem Cells Play in Regenerative Medicine?
Regenerative medicine is a rapidly evolving field that harnesses the remarkable properties of stem cells to heal and restore damaged or diseased tissues and organs. By leveraging the self-renewal and differentiation capabilities of stem cells, researchers are developing innovative therapies that hold the potential to revolutionize how we approach the treatment of a wide range of medical conditions.
Stem cells are at the heart of regenerative medicine, offering a transformative approach to tissue repair and organ restoration.
- Tissue Engineering: Stem cells are being used as building blocks for the creation of artificial tissues and organs, known as tissue engineering. By seeding stem cells onto specialized scaffolds, researchers can guide the formation of functional tissue structures that can be implanted to replace or repair damaged body parts.
- Organ Regeneration: The ability of stem cells to differentiate into various cell types has led to the exploration of stem cell-based therapies for organ regeneration. Researchers are working on developing techniques to grow replacement organs, such as kidneys, livers, and hearts, using the patient's own stem cells, reducing the risk of rejection.
- Wound Healing: Stem cells have demonstrated the capacity to accelerate the healing process of wounds, ulcers, and other types of tissue damage. By applying stem cell-based treatments, clinicians aim to enhance the body's natural healing response and promote the regeneration of healthy tissue.
The remarkable advancements in stem cell technology have opened up unprecedented opportunities in the realms of disease treatment, tissue regeneration, and personalized medicine. As researchers continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, the future of stem cell-based therapies holds the promise of transforming the way we approach some of the most challenging health conditions.
The Ethical Debate Surrounding Stem Cell Research
What Are the Ethical Concerns Surrounding Stem Cell Research?
Stem cell research has long been a controversial topic, raising a host of ethical concerns that continue to be debated by scientists, policymakers, and the general public. As this field of study has advanced, so too have the ethical quandaries it presents.
At the heart of the debate are questions about the moral status of embryonic stem cells and the appropriate use of this type of biological material.
- Embryonic stem cells are derived from human embryos, which some view as equivalent to human life. This raises concerns about the destruction of potential human life for research purposes.
- There are also issues around the informed consent of donors, the commercialization of stem cell products, and the potential for stem cell research to enable the genetic engineering of humans.
- Additionally, there are concerns about the equitable access to any therapies or treatments that may result from stem cell research, and whether these would only benefit the wealthy and privileged.
These are complex and contentious issues without easy answers. As stem cell research continues to progress, it is crucial that we engage in thoughtful, nuanced discussions to navigate the ethical minefield and ensure this powerful technology is developed responsibly.
How Do Different Countries Approach Stem Cell Ethics?
The ethical debates surrounding stem cell research have played out differently across the globe, with various countries taking divergent approaches based on their cultural, religious, and political landscapes.
In the United States, for example, stem cell research has been a hotly contested issue, with federal funding restrictions and shifting policies depending on the administration in power.
- During the George W. Bush administration, federal funding for embryonic stem cell research was limited to a small number of existing cell lines. This prompted many scientists to seek funding from private sources or move their research abroad.
- The Obama administration later lifted these restrictions, allowing for broader federal funding of embryonic stem cell research. However, the debate continues, with some states passing laws to limit or ban certain stem cell techniques.
- In contrast, countries like the United Kingdom, Sweden, and China have taken a more permissive approach, allowing for the derivation of new embryonic stem cell lines and the use of somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) for research purposes.
These different national policies reflect the nuanced and complex ethical considerations at play, underscoring the need for ongoing dialogue and the development of international guidelines to ensure stem cell research progresses in an ethically responsible manner.
What Are the Arguments For and Against Stem Cell Research?
The ethical debate surrounding stem cell research encompasses a wide range of arguments, both in favor of and against the pursuit of this scientific endeavor.
Proponents of stem cell research often highlight the immense potential of this field to unlock new medical treatments and therapies.
- Stem cells have the unique ability to develop into a wide range of specialized cell types, making them a promising tool for regenerative medicine. Researchers hope to harness this potential to treat conditions like spinal cord injuries, Parkinson's disease, and type 1 diabetes.
- Embryonic stem cells, in particular, are seen as a valuable resource for understanding human development and uncovering the mechanisms underlying genetic and congenital disorders.
- Advances in stem cell research could also lead to breakthroughs in the study of cancer, neurological diseases, and other debilitating conditions, potentially saving and improving countless lives.
On the other hand, opponents of stem cell research raise concerns about the moral status of embryonic stem cells and the ethical implications of their use.
- Many believe that the destruction of human embryos, even for research purposes, is a violation of the right to life and a form of unacceptable instrumentalization of human life.
- There are also fears that stem cell research could lead to the exploitation of vulnerable populations, such as egg donors, and the commercialization of human biological material.
- Some critics argue that alternative, non-embryonic stem cell sources, such as adult stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells, should be the focus of research efforts, as they do not raise the same ethical concerns.
The ethical debate surrounding stem cell research is multifaceted and ongoing. As the field continues to evolve, it is crucial that we engage in thoughtful, nuanced discussions to ensure that the development of this powerful technology is guided by a strong ethical framework that upholds the dignity and well-being of all.
Unleash the Power of Nature's Finest: Our Organic Skincare Collection
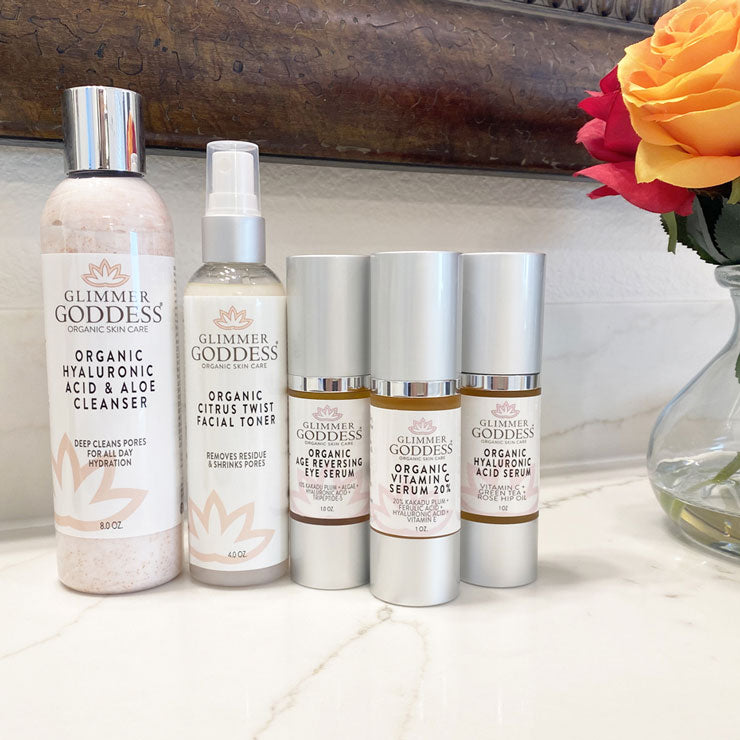
Organic Apple Stem Cell Renewal Moisturizer 🍎
Experience deep hydration and age-defying benefits with our Pregnancy-Safe Apple Stem Cell Moisturizer, expertly formulated to nourish, protect, and revitalize sensitive skin during pregnancy.
This lightweight yet deeply moisturizing face cream is powered by a blend of nature's most effective ingredients, including:
- Apple, Lingonberry, Orchid, and Orange Stem Cells to boost collagen, smooth fine lines, and enhance skin elasticity
- Hyaluronic Acid and Squalane to lock in moisture for long-lasting hydration
- Camu Camu Extract, a natural source of Vitamin C, to brighten and even skin tone without irritation
- Jojoba Oil and Aloe Vera to calm redness, soothe dryness, and reinforce the skin's barrier for a soft, supple, and radiant glow
Organic Apple Stem Cell Serum for Anti-Aging 🍎
Experience youthful, radiant skin with our Apple Stem Cell Anti-Wrinkle Serum. This potent formula combines multiple organic stem cells for the most hydrating serum available.
This natural serum features a powerful blend of regenerative ingredients that work in synergy to revitalize and rejuvenate your skin, delivering visible anti-aging results:
- Regenerative apple stem cells to stimulate skin cell renewal and reduce wrinkles
- Antioxidant-rich lingonberry stem cells to protect against environmental stressors and UV damage
- Hydrating orchid stem cells to enhance moisture retention and firm the skin
- Brightening orange stem cells to boost collagen and promote a luminous complexion
Pair the power of apple stem cells with an anti-aging cream for the best results.

Organic Illuminating Fruit Stem Cell Glow CC Cream Reef-Safe SPF 45 🌺
Experience the ultimate in skincare with our Organic Illuminating Fruit Stem Cell Glow Cream. This advanced formula harnesses the power of nature's finest ingredients to deliver a radiant complexion while providing superior protection.
This all-in-one Fruit Stem Cell cream nourishes, protects, and enhances your skin's natural beauty with a range of transformative benefits:
- Powerful Fruit Stem Cells (Ligonberry, orchid, and orange) to reduce wrinkles, spots, firmness loss, dehydration, and roughness
- Hydrating and Conditioning Rosemary leaf extract and algae extract for a smoother, softer feel
- Advanced Hydration from Matrixl 3000, Argirelene, and Tripeptide-5 to instantly boost hydration levels and minimize fine lines and wrinkles
- Brightening Effect with ultrafine brightening pearls and glimmering mica minerals to enhance luminosity and impart a universally flattering glow
- High SPF 45 Protection that is Reef-Safe, shielding your skin from harmful UV rays
Unlock your skin's potential and embrace the transformative power of nature with our Organic Skincare Collection. Infused with the most advanced plant-based ingredients, each product in our line-up is designed to nourish, protect, and revitalize your skin, leaving you with a radiant, youthful glow. 🌟
From our Apple Stem Cell Moisturizer that deeply hydrates and diminishes the signs of aging, to our Fruit Stem Cell CC Cream that provides reef-safe SPF 45 protection while imparting a luminous, glowing complexion, our collection is the ultimate solution for achieving healthy, beautiful skin.
Indulge in the synergistic benefits of our potent, natural formulas and experience the difference that plant-powered skincare can make. Unlock your skin's full potential and let your natural beauty shine through.
Q&A
What are the main types of stem cells?
Stem cells are classified into four main types: 1) Embryonic stem cells, which are pluripotent and derived from early-stage embryos; 2) Adult stem cells, which are multipotent and found in various tissues; 3) Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which are adult cells reprogrammed back to a pluripotent state; and 4) Cord blood stem cells, harvested from umbilical cords and valuable for blood-forming applications.
How do stem cells contribute to tissue regeneration?
Stem cells contribute to tissue regeneration through their abilities of self-renewal and differentiation. They can migrate to areas of injury, differentiate into specialized cell types, and secrete signaling molecules that promote healing and repair of damaged tissues.
What are the latest advancements in stem cell technology?
Recent advancements include the development of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which have revolutionized research by allowing adult cells to revert to a pluripotent state. Additionally, progress in directed differentiation has enabled scientists to create specific cell types for regenerative therapies, while continued exploration in embryonic stem cell methods expands potential applications.
What ethical concerns surround stem cell research?
Ethical concerns include the moral status of embryonic stem cells, the potential destruction of embryos for research, issues of informed consent from donors, commercialization of stem cell therapies, and equitable access to treatments derived from stem cell research.
How do different countries regulate stem cell research?
Countries vary in their regulations surrounding stem cell research based on cultural, religious, and political perspectives. The United States has seen restrictions and allowances shift with different administrations. In contrast, countries like the UK and Sweden have adopted more permissive stances, permitting new lines of embryonic stem cell research.
The journey of stem cell research is one of immense potential and promise, unraveling exciting opportunities in regenerative medicine. As we navigate the complex ethical landscape, it is imperative that we advocate for responsible research practices and embrace the transformative capabilities of stem cells in healing and rejuvenating healthcare. The future of medicine is bright, and stem cells are at the forefront of it.